Introduction to Digital Diagnostic Monitoring
Cisco GLC-SX-MMD transceiver is a 1000BASE-SX SFP optical transceiver. This hot-swappable input/output device plugs into a Gigabit Ethernet port or slot and allows the port to be linked with the network via multimode optical fiber. Cisco GLC-SX-MMD transceiver is a replacement of Cisco GLC-SX-MM transceiver. The module numbers of these two SFP transceivers differ only in one letter "D". This "D" mainly represents a function named DDM, which is inherited by many fiber optic transceivers offered today. What is this DDM function? Why this DDM function can offer GLC-SX-MMD transceiver advantages over GLC-SX-MM transceiver? This article will help you understand DDM.

DDM is short for digital diagnostic monitoring according to the industry standard MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) SFF-8472 and is also known as DOM (digital optical monitoring). When selecting fiber optic transceivers today, you can choose transceiver modules with or without DDM/DOM function. Most of fiber optic transceivers now are with the DDM function. This technology allows the user to monitor real-time parameters of the fiber optic transceivers, like optical input/output power, temperature, laser bias current, and transceiver supply voltage, and so on.
DDM can provide component monitoring on transceiver applications in details. The SFF-8472 added DDM interface and outlined that DDM interface is an extension of the serial ID interface defined in GBIC specification, as well as the SFP MSA. DDM interface includes a system of alarm and warning flags which alert the host system when particular operating parameters are outside of a factory set normal operating. Thus, DDM interface can also enable the end user with the capabilities of fault isolation and failure prediction. This part will explain what can be done with DDM.
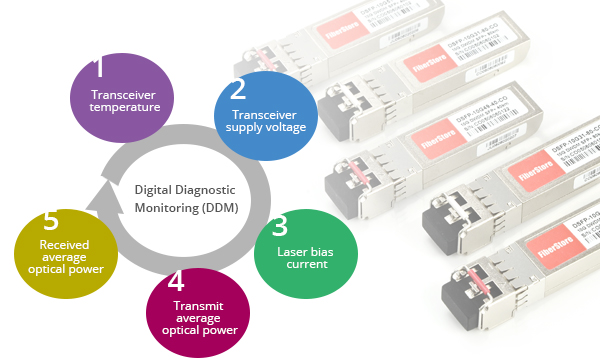
Component Monitoring: DDM enables the end user to monitor key parameters in the performance of fiber optic transceivers. The real-time diagnostic parameters can be monitored to alert the system when the transceiver's specified operating limits are exceeded and compliance cannot be ensured. These key parameters includes:
- Transceiver temperature
- Transceiver supply voltage
- Laser bias current
- Transmit average optical power
- Received optical modulation amplitude (OMA) or Average Optical Power
Fault Isolation: DDM function can be used to isolate the particular location of fault in fiber optic network systems. Combining the DDM interface status flags, transceiver hard pins and diagnostic parametric monitor data the specific location and cause of a link failure can be pinpointed.
Failure Prediction: DDM can also be used to help predict failure on fiber optic links, which is based on the transceiver parametric performance. Although, this application is not yet fully mature, but there is still room for improvement. There are two basic types of failure conditions that can be seen on fiber optic transceivers. One is device faults, which means non-operation or malfunction of a device and is typically applied to transmitter performance, due to nature of semiconductor lasers. The other is high error rate conditions, which means operating conditions are such that a fiber optic transceiver is operating at its signal-to-noise limit, and is applied more to fiber optic receiver performance.
Providing parameter monitoring, fault isolation, and failure prediction, fiber optic transceivers with DDM help to ensure that the business can be proactive in preventative maintenance of the network and ensure business continuity. So it would be easy to explain why modern transceivers are with DDM and why GLC-SX-MMD SFP optical transceiver can replace GLC-SX-MM SFP optical transceiver. It is an irresistible trend of industry and technology development. Although fiber optic transceivers with DDM function are much more popular than those without DDM, some users still choose the older optical transceivers in consideration of the upgrading costs.